The Forex market, with its vast liquidity and 24/5 operation, is a dynamic arena for traders worldwide. A fundamental concept that every trader must grasp to navigate this market effectively is what is spread in Forex. The spread refers to the difference between the bid price (the price at which you can sell a currency) and the ask price (the price at which you can buy a currency). This small yet critical factor influences trading costs, profitability, and broker selection. This article delves into the meaning of spread, its types, its impact on trading, and how to optimize your Forex strategy with this knowledge.

Understanding the Basics of Spread in Forex
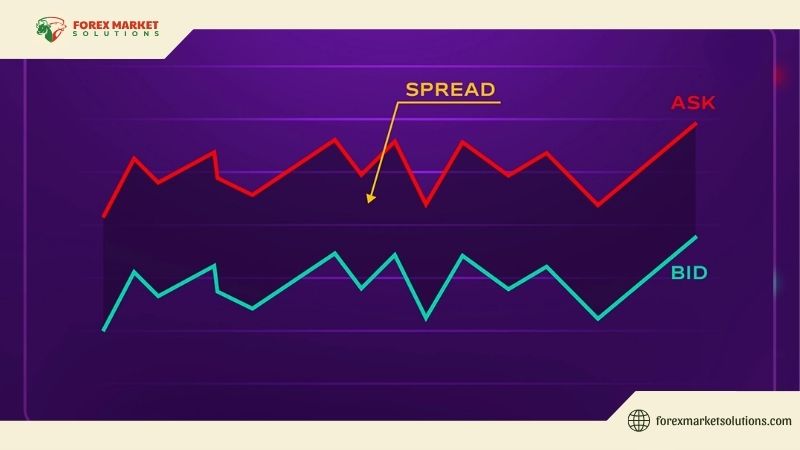
To comprehend what is spread in Forex, it’s essential to break it down to its core. The spread is essentially the transaction cost imposed by brokers, reflecting the market’s liquidity and volatility. For example, if the EUR/USD bid price is 1.1050 and the ask price is 1.1052, the spread is 2 pips. Pips are the smallest price movement in Forex, typically the fourth decimal place in most currency pairs.
The spread exists because brokers facilitate trades between buyers and sellers, and this difference compensates them for their services. In the highly liquid Forex market, where transactions occur instantly, what is spread in Forex becomes a key determinant of trading efficiency, especially for high-frequency traders or those dealing with exotic pairs.
Why Spread Matters in Forex Trading
The spread is a vital consideration when exploring what is spread in Forex, as it directly affects your profitability. A narrower spread means lower costs, allowing more of your capital to work toward potential gains. Conversely, a wide spread increases the cost of entering and exiting trades, eating into profits, particularly for scalpers who execute numerous trades daily.
Market conditions influence spread size. During high volatility—such as after major economic announcements like Non-Farm Payroll data—spreads widen due to increased risk for brokers. Understanding what is spread in Forex helps traders anticipate these fluctuations and adjust their strategies to minimize costs and maximize returns.
Types of Spreads in Forex
Diving deeper into what is spread in Forex reveals different types that traders encounter. The most common is the fixed spread, where the broker maintains a constant difference between bid and ask prices regardless of market conditions. This offers predictability, appealing to beginners, but may not reflect real-time market dynamics.
Variable spreads, on the other hand, fluctuate based on market liquidity and volatility. They are typically tighter during stable periods and wider during news events, aligning more closely with interbank rates. Some brokers offer zero spreads with a commission per trade, catering to advanced traders seeking transparency. Recognizing these variations is crucial to grasping what is spread in Forex and choosing the right trading environment.
How Spread Is Calculated
Calculating what is spread in Forex involves a simple formula: Spread = Ask Price – Bid Price. For instance, if the bid price for GBP/USD is 1.3050 and the ask price is 1.3053, the spread is 3 pips. In terms of monetary value, multiply the pip difference by the lot size and the currency pair’s pip value. For a standard lot (100,000 units), a 1-pip spread on EUR/USD (where 1 pip = $10) costs $10 per trade.
Brokers may express spreads in pips or points, depending on the platform. Understanding this calculation helps traders assess costs accurately, a practical application of what is spread in Forex that influences trade planning and profitability.
Factors Influencing Spread Size
Several factors shape what is spread in Forex, impacting its width. Liquidity is a primary driver—major pairs like EUR/USD or USD/JPY, with high trading volumes, typically have tighter spreads due to abundant market participants. Exotic pairs, such as USD/TRY, with lower liquidity, often feature wider spreads.
Volatility plays a significant role, with spreads widening during economic data releases, central bank announcements, or geopolitical crises. Broker type also matters: market maker brokers may offer fixed spreads, while ECN (Electronic Communication Network) brokers provide variable spreads reflecting real-time market conditions. Grasping these influences enhances your understanding of what is spread in Forex.
The Impact of Spread on Trading Costs
The spread directly affects trading costs, making what is spread in Forex a critical metric for cost management. For a day trader executing 10 trades with a 2-pip spread on EUR/USD, the total cost is 20 pips, or $200 for a standard lot. Over time, these costs accumulate, reducing net profits if not accounted for.
Scalpers, who thrive on small price movements, are particularly sensitive to spread size, as wide spreads erode their slim margins. Long-term traders may feel less impact but still benefit from minimizing costs. Recognizing what is spread in Forex allows traders to select brokers and strategies that align with their trading style and budget.
Choosing a Broker Based on Spread
Selecting a broker hinges on understanding what is spread in Forex and its implications. ECN brokers often offer the tightest spreads, sometimes as low as 0.1 pips, though they may charge commissions. Market maker brokers provide fixed spreads, which can range from 1 to 3 pips, suitable for beginners seeking stability.
Compare spreads across brokers for your preferred currency pairs during different market conditions. Check for hidden fees, such as overnight swap charges, that could offset narrow spreads. A broker’s reputation, regulation, and execution speed also matter when leveraging what is spread in Forex to optimize your trading experience.
Spread and Market Hours
Market hours significantly influence what is spread in Forex. Spreads are typically tightest during the overlap of major sessions, like the London-New York overlap (8 AM to 12 PM EST), when liquidity peaks. During the Asian session or weekends, when trading volume drops, spreads widen due to lower activity.
Economic events, such as interest rate decisions, can cause temporary spikes in spreads as brokers adjust to heightened volatility. Traders can use this knowledge to schedule trades during optimal hours or avoid high-spread periods, a strategic use of what is spread in Forex.

Strategies to Minimize Spread Costs
Minimizing spread costs is a practical application of what is spread in Forex. Trade during high-liquidity sessions, such as the London or New York opens, to benefit from tighter spreads. Avoid trading immediately after major news releases, when volatility and spreads peak, unless you’re prepared for rapid moves.
Focus on major currency pairs with naturally low spreads, like EUR/USD or USD/JPY, rather than exotic pairs. Use limit orders to enter trades at desired prices, reducing the impact of wide spreads. These tactics help traders optimize profitability while understanding what is spread in Forex.
The Role of Spread in Risk Management
Spread plays a role in risk management, a key aspect of what is spread in Forex. Wider spreads increase the breakeven point for trades, requiring larger price movements to profit. This risk is higher for short-term strategies like scalping, where small spreads are critical.
Incorporate spread into your risk-reward calculations. For example, with a 2-pip spread, ensure your target profit exceeds the spread by a comfortable margin, such as 10 pips, for a 5:1 reward-to-risk ratio. This approach balances cost and potential gain, enhancing your grasp of what is spread in Forex.
Spread and Trading Platforms
Trading platforms influence what is spread in Forex by determining how spreads are displayed and executed. MetaTrader 4 and 5, widely used in Forex, show real-time bid-ask spreads, allowing traders to monitor costs. ECN accounts on these platforms often provide raw spreads plus a commission, offering transparency.
Choose a platform with fast execution to avoid slippage, which can widen effective spreads during volatile periods. Familiarity with your platform’s spread display ensures you can react swiftly, a practical skill tied to what is spread in Forex.
Common Misconceptions About Spread
Misunderstandings about what is spread in Forex can mislead traders. One myth is that a zero-spread account eliminates costs, ignoring commissions that may apply. Another is that fixed spreads are always better, overlooking their lack of alignment with market conditions.
Some believe spreads are uniform across brokers, but they vary based on liquidity and broker model. Clearing these misconceptions with research helps traders make informed choices, deepening their understanding of what is spread in Forex.

Monitoring and Adapting to Spread Changes
Staying adaptable is key to leveraging what is spread in Forex. Regularly monitor spread fluctuations using your broker’s platform or third-party tools like Myfxbook. Adjust your trading schedule to avoid wide spreads during low-liquidity hours or major news events.
Keep abreast of market conditions, such as central bank policies or economic data releases, that affect spreads. This proactive approach ensures you optimize costs and maintain profitability, a dynamic aspect of what is spread in Forex.
Master Spread for Forex Success
Grasping what is spread in Forex is fundamental to navigating the currency market effectively. From understanding its role as a trading cost to selecting brokers and managing risks, the spread influences every aspect of your strategy. By minimizing costs, adapting to market conditions, and using the right tools, you can enhance your trading performance and profitability.
Ready to refine your Forex trading skills? Visit Forex Market Solutions for expert insights, strategies, and resources to succeed. Follow our website today to master what is spread in Forex and elevate your trading journey!