In the world of blockchain technology, Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) has emerged as a promising alternative to traditional blockchain systems. With its ability to process transactions quickly and efficiently, DAG is gradually being widely applied in cryptocurrency platforms, offering notable advantages in terms of speed, cost, and energy efficiency. But what is DAG Blockchain? Why is it considered the future of decentralized transactions? Let’s explore this in detail in the article below.
What is DAG Blockchain?
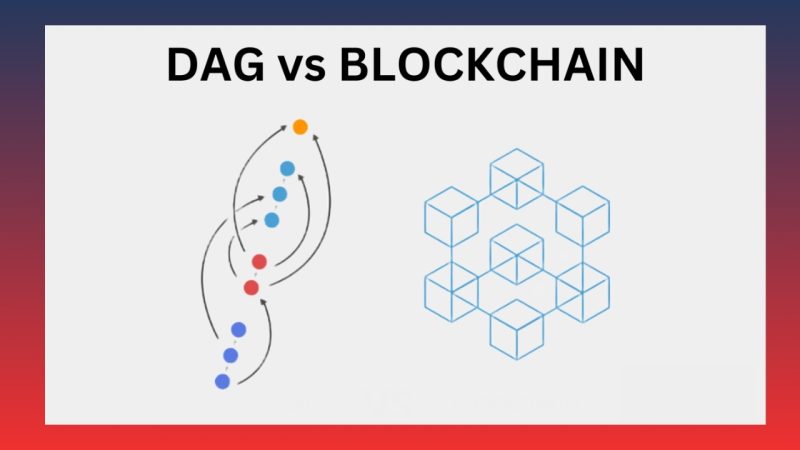
DAG stands for Directed Acyclic Graph, a directed, non-circular graph structure. This new model in the blockchain technology world replaces the traditional method of linking data blocks in a chain with a graph where transactions are linked to one another. This structure helps minimize transaction validation delays while saving energy and costs, as there is no need for miners, unlike in traditional blockchain systems.
One of the major advantages of DAG Blockchain is its ability to process transactions almost instantly. Transactions are validated simultaneously without waiting for new blocks to be added to the chain. This reduces congestion and transaction costs while increasing the scalability of the network without affecting performance.
Platforms using DAG can operate much faster than traditional blockchain systems. Since there is no need to create new blocks, the transaction processing becomes more flexible and can achieve higher speeds, which is crucial for systems with large transaction volumes, such as cryptocurrencies or the Internet of Things (IoT).

The difference between DAG Blockchain and traditional Blockchain
One of the key differences between DAG Blockchain and traditional Blockchain lies in how transactions are organized and validated. In a traditional blockchain, data is organized into blocks, each containing a set number of transactions, and these blocks are linked in a chain. This means transactions must wait for new blocks to be created before they can be validated.
In contrast, in DAG Blockchain, transactions are validated directly through points in the graph, without relying on blocks. Each transaction can reference one or more previous transactions in the DAG, which helps reduce congestion and improve transaction speed. This model allows DAG Blockchain to process transactions simultaneously without facing the congestion issues found in traditional blockchains.
Another distinction is that DAG Blockchain does not require mining to create blocks, helping reduce energy consumption and transaction costs. The absence of miners to validate transactions saves computational resources, making it a more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly solution compared to traditional blockchains.
How DAG Blockchain works?
DAG Blockchain operates based on a directed graph model, where each transaction is represented by a point (node) in the graph. Each point can be directly linked to one or more prior points, indicating the relationship between transactions. Transactions are not grouped into blocks; instead, they are validated simultaneously in the system without waiting for new blocks to be added.
This brings clear benefits in terms of speed and cost. Since no blocks need to be created, the time it takes for a transaction to be validated and added to the system is very fast. While traditional blockchains require mining to validate transactions, DAG can function without miners. This not only helps save resources but also reduces transaction costs and processing times.
It’s important to note that although the DAG model does not require mining, transactions in DAG Blockchain still need to be validated to ensure safety and reliability. Transactions can be validated by nodes in the system or through alternative consensus mechanisms, helping maintain security and decentralization within the network.
Benefits of DAG Blockchain in Cryptocurrency
DAG Blockchain offers numerous advantages over traditional Blockchain, particularly in the cryptocurrency sector. Here are some key benefits:
- Faster transactions: With the ability to process transactions simultaneously without needing to create new blocks, DAG enables transactions to occur quickly without congestion. This is critical in the cryptocurrency environment, where transaction speed is a decisive factor in platform success.
- Energy efficiency: One of the major issues with traditional Blockchain is the energy consumption during mining. DAG reduces mining requirements and energy consumption, making the network more environmentally friendly.
- Lower transaction fees: Because there are no blocks to create and validate transactions, transaction fees in DAG Blockchain are typically much lower than in traditional Blockchain. This is especially important for cryptocurrency platforms with large transaction volumes.
- Better scalability: DAG can easily scale without facing congestion issues as transaction volumes increase. This makes DAG an ideal solution for applications that require flexible scalability.

Prominent applications of DAG Blockchain
DAG Blockchain technology is increasingly attracting attention within the cryptocurrency community and technology industries due to its ability to enhance efficiency, scalability, and reduce transaction costs. Below are some noteworthy applications of DAG Blockchain in the cryptocurrency world:
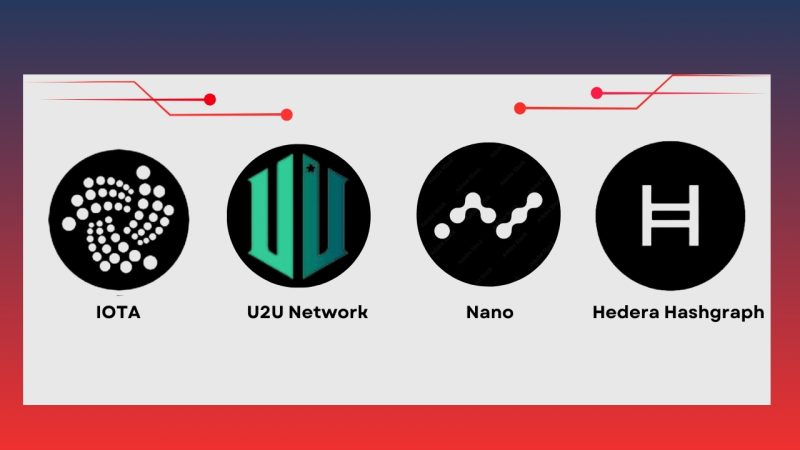
- IOTA: IOTA is a pioneering project that uses DAG technology to create an Internet of Things (IoT) platform. Instead of using blocks like traditional blockchains, IOTA uses the Tangle model, a form of DAG, to validate transactions. Each transaction in IOTA is performed by referencing two previous transactions, which not only accelerates transaction speed but also eliminates transaction fees. This model helps reduce transaction congestion, a common issue in traditional blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Nano: Nano is a cryptocurrency built on a block-lattice platform, combining DAG and blockchain. In Nano, each user has their own blockchain to handle their transactions, with each transaction being recorded in both the sender’s and receiver’s blockchains instead of a central block. This not only speeds up transactions but also reduces transaction costs, as Nano does not require miners or high mining fees. Nano’s network is completely free of transaction fees, making it an attractive option for microtransactions.
- Hedera Hashgraph: Hedera Hashgraph is a DAG blockchain project designed to provide a distributed, fast, and secure platform for enterprise applications. Hashgraph uses a DAG-based consensus protocol to process thousands of transactions per second without miners’ involvement. This technology also allows Hedera Hashgraph applications to scale efficiently while being more energy-efficient than traditional blockchains that rely on proof-of-work.
- U2U Chain: U2U Chain is a rapidly developing blockchain project that applies DAG technology to optimize crucial elements in Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN). With DAG, U2U Chain can process millions of transactions in fields such as IoT, GPU computing, and decentralized storage without facing the speed and scalability limitations of traditional blockchains. This network does not require mining, saving energy and providing faster transaction speeds. U2U Chain also helps reduce transaction costs and optimize the performance of decentralized networks, creating new opportunities for blockchain applications in industrial and decentralized environments.
Challenges and limitations of DAG Blockchain
Despite its many advantages, DAG Blockchain also faces several challenges and limitations:
- Smart Contract support: DAG Blockchain does not yet support smart contracts as robustly as traditional Blockchain, which limits its application in areas like DeFi. While projects like IOTA are working to improve this feature, developing a fully functional smart contract ecosystem remains a significant challenge.
- Lack of full decentralization: Although DAG Blockchain is decentralized, some systems may still be controlled by a small group, raising concerns about transparency and security. This needs to be addressed to maintain decentralization, especially in financial applications.
- Scalability and consensus: While DAG is scalable, maintaining stability as transaction volumes increase remains a challenge. An effective and secure consensus mechanism is required to ensure network stability.
- Lack of compatibility and infrastructure support: DAG Blockchain is not fully compatible with existing tools and infrastructure, making it difficult and costly to transition from traditional blockchains. This limits the widespread adoption of DAG technology.
- Security concerns: Although DAG does not require mining, the lack of strong security mechanisms may expose the network to attacks. Issues like double-spending and Sybil attacks remain concerns that need to be addressed.
The future of DAG Blockchain
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) Blockchain is a technology gradually changing how we view and implement blockchain in distributed systems. While there are still some challenges to overcome, the future of DAG Blockchain is promising, with many potential applications across various sectors. Below are trends and prospects for DAG Blockchain in the future:

- Development and refinement of technology: While DAG Blockchain offers several advantages, some technical issues still need to be resolved, such as developing stronger consensus mechanisms and supporting complex features like smart contracts. However, research projects focused on DAG, such as IOTA, Nano, and Hedera Hashgraph, are continually improving this technology. In the future, DAG Blockchain will expand its ability to support complex transactions and decentralized applications (dApps), making it a more comprehensive solution.
- Enhanced scalability: A major issue faced by traditional blockchains is scalability. As the number of users and transactions increases, blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum can experience congestion and rising transaction fees. In contrast, DAG Blockchain is designed to process transactions without blocks, offering better scalability. As more projects and applications are developed on DAG platforms, we can expect the scaling of these systems without significant congestion issues.
- Application in the Internet of Things (IoT): One area where DAG Blockchain could thrive in the future is IoT. IoT requires the rapid and efficient processing of vast amounts of data and transactions. IOTA, a leading platform using DAG, has targeted this technology to optimize transactions in IoT environments, where millions of devices must communicate and execute transactions almost simultaneously. DAG Blockchain can reduce latency and transaction costs in IoT systems, creating significant improvements in performance and scalability.
- Replacing traditional Blockchain in financial applications: In the future, DAG Blockchain could become a more reliable choice for financial applications. With fast, low-cost transactions, it could easily replace traditional blockchains in financial transactions. Current cryptocurrency platforms still face issues with transaction speed and high costs, but DAG Blockchain can address these problems by processing transactions simultaneously without the need for blocks.
- Support for decentralized and distributed models: One of the key features of DAG Blockchain is decentralization. DAG reduces dependency on miners and allows transactions to be validated quickly without complex mining mechanisms. This paves the way for developing decentralized models and enhancing security and transparency in systems. As decentralized models become more common, DAG Blockchain can serve as the foundation for new applications in decentralized finance (DeFi), decentralized exchanges (DEX), and even decentralized storage solutions.
Through this article, you now have the answer to the question “What is DAG Blockchain?” DAG Blockchain is a groundbreaking technology that brings significant improvements in processing transactions quickly, saving energy, and reducing costs. Although it still faces some challenges, DAG is gradually proving its potential for the future, especially in applications that require high speed and scalability. With its outstanding advantages, DAG Blockchain could become a pioneering technology in the blockchain revolution in the coming years.
Don’t forget to continue following Forex Market Solutions for daily updates and insights on technology and investment markets.
